In view of the importance of export credit in maintaining the pace of export growth in India, RBI has initiated several measures to ensure timely flow of credit to the export sector. These measures, include rationalization of export credit interest rates, special financial package for exporters, different types of Pre-shipment Finance credits and flexibility of repayment of pre-shipment credit Etc;
The advances given by commercial banks for export financing are in the form of:
Pre-shipment finance – advance extended by banks before shipment of goods.
Post-shipment finance – advance extended by banks after shipment of goods.
What is Pre-shipment finance for exports?
Pre-Shipment Finance is an advance extended by banks to an exporter for the purpose of buying, manufacturing, processing, packing, and shipping goods to overseas buyer. It is also known as packing credit facility,
Any exporter, having a firm export order placed with him by his foreign buyer or an irrevocable letter of credit opened in his favor, can approach a bank for availing of packing credit.
An advance taken by an exporter is required to be liquidated within 180 days from the date of its commencement by negotiation of export bills or receipt of export proceeds in an approved manner. Thus, packing credit is essentially a short-term advance.
Normally, banks insist upon their customers to lodge with them irrevocable letters of credit opened in favor of the customers by the overseas buyers. The letter of credit and firm sale contracts not only serve as evidence of a definite arrangement for realization of the export proceeds but also indicate the amount of finance required by the exporter
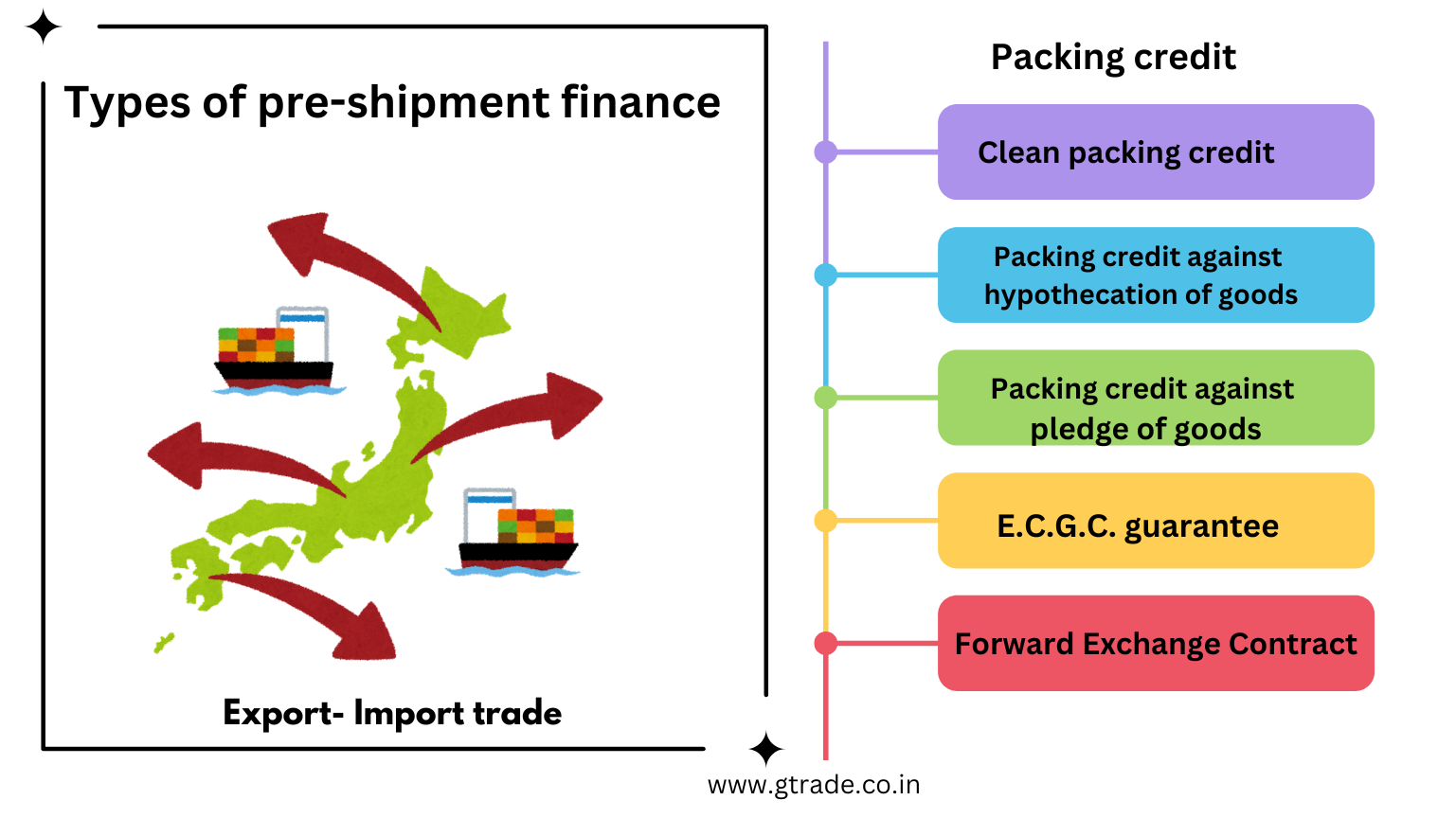
The types of pre-shipment finance/packing credit include:
| Types of Packing Credit | |
| 1 | Clean packing credit |
| 2 | Packing credit against hypothecation of goods |
| 3 | Packing credit against pledge of goods: |
| 4 | E.C.G.C. guarantee |
| 5 | Forward Exchange Contract |
1. Clean packing credit:
This is an advance made available to an exporter only on production of a firm export order or a letter of credit without exercising any charge or control over raw material or finished goods.
It is a clean type of export advance. Each proposal is weighed according to particular requirements of the trade and credit worthiness of the exporter.
A suitable margin has to be maintained. Also, Export Credit Guarantee Corporation (ECGC) cover should be obtained by the bank.
It covers production costs, including purchase of raw materials, labor, transportation, as well as packing costs of the goods for export.
2. Packing credit against pledge of goods:

A packing credit loan (pledge) is a type of pre-shipment finance provided to businesses to cover the costs of production and packing of goods being exported.
Export finance is made available on certain terms and conditions where the exportable finished goods are pledged to the banks with approved clearing agents who will ship the same from time to time as required by the exporter.
The possession of the goods so pledged lies with the bank and is kept under its lock and key.
A pledge is a legal agreement in which a borrower gives the lender the right to seize and sell certain assets if the borrower fails to repay the loan.
In the case of a packing credit loan (pledge), the goods being produced or exported are used as collateral for the loan.
3. Packing Credit Loan (Hypothecation):
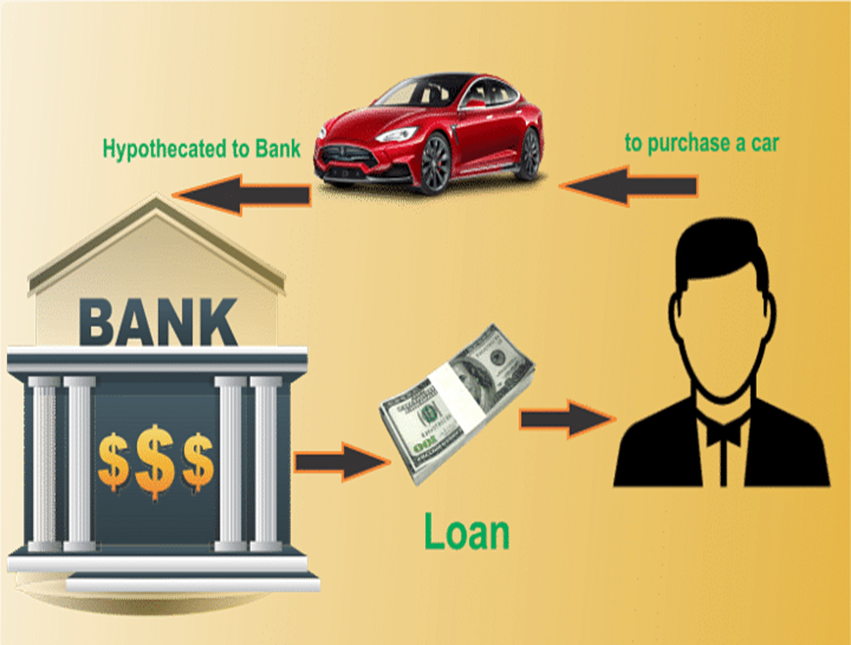
• Export finance is made available on certain terms and conditions where the exporter has pledge able interest and the goods are hypothecated to the bank as security with stipulated margin.
• At the time of utilizing the advance, the exporter is required to submit, along with the firm export order or letter of credit relative stock statements and thereafter continue submitting them every fortnight and/or whenever there is any movement in stocks.
• Hypothecation occurs when an asset is pledged as collateral to secure a loan.
• The owner of the asset does not give up title, possession, or ownership rights, such as income generated by the asset.
• However, the lender can seize the asset if the terms of the agreement are not met. Hypothecation is different from a mortgage, lien, or assignment.
The loan is typically extended by a bank or financial institution and secured by a hypothecation agreement, which is a legal document that allows the lender to seize the goods being financed if the borrower defaults on the loan.
4. E.C.G.C. guarantee:

Any loan given to an exporter for the manufacture, processing, purchasing, or packing of goods meant for export against a firm order qualifies for the packing credit guarantee issued by Export Credit Guarantee Corporation of India.
The ECGC Guarantees assure the banks, in the event of an exporter failing to discharge his liabilities to the bank, the ECGC corporation would cover a major portion of the bank’s loss.
5. Forward exchange contract:
Another requirement of packing credit facility is that if the export bill is to be drawn in a foreign currency, the exporter should enter into a forward exchange contract with the bank, thereby avoiding risk involved in a possible change in the rate of exchange.
Pre-Shipment Credit in Foreign Currency (PCFC):
In India, pre-shipment credit in foreign currency (PCFC) is a type of short-term loan that banks and financial institutions extend to cover the cost of purchasing raw materials, transportation and are often used by businesses to finance the export of goods or services to foreign countries.
The loan is typically secured by the goods or services being exported and denominated in the importing country’s currency.
What are the Documents Required for Pre-Shipment Finance?
In India, the documents required for pre-shipment finance will vary depending on the export transaction and the type of financing being used. However, some common documents that may be required include:
| Export sales contract | This is the main document outlining the terms and conditions of the export transaction, including the goods being sold, the price, and the payment terms. |
| Proforma invoice | This is a preliminary invoice that provides an estimate of the total cost of the goods being exported. A proforma invoice may be used to obtain financing or as a basis for the final invoice. |
| commercial invoice | which is a detailed list of the goods being exported and their associated costs. |
| Letter of credit | This is a financial instrument issued by a bank on behalf of the buyer, which guarantees payment to the exporter once the goods have been shipped and the required documents have been presented. |
| Shipping documents | These documents include the bill of lading, which is a receipt for the goods being shipped, |
| Insurance documents | These documents, such as a marine insurance policy, protect against the risk of damage or loss to the goods during shipping. |
| Certificates of origin | The certificates of origin documents are essential to show that the exported goods originate from a specific country and may be required for certain types of goods or markets. |
What are the Benefits of Pre-shipment finance?
Improved cash flow:
Pre-shipment finance can help businesses to improve their cash flow by providing the funds needed to purchase and transport goods or services for export.
Enhanced competitiveness:
Pre-shipment finance can enable businesses to better compete in international markets by providing the funds needed to take advantage of export opportunities.
Increased flexibility:
It can provide businesses with greater flexibility in their operations by allowing them to finance the purchase and transportation of goods or services for export as needed.
Reduced risk:
Pre-shipment finance allows businesses to reduce the risk of financial losses by providing the funds needed to purchase and transport goods or services for export.
Improved supplier relationships:
It can help businesses to strengthen their relationships with suppliers by providing the funds needed to purchase goods or services for export on time.
summary:
Pre-shipment finance allow businesses to manage their financial resources better and reduce the risk of financial difficulties. It helps businesses to manage their risks better, improve their competitiveness and profitability. and increase their chances of success in international markets.