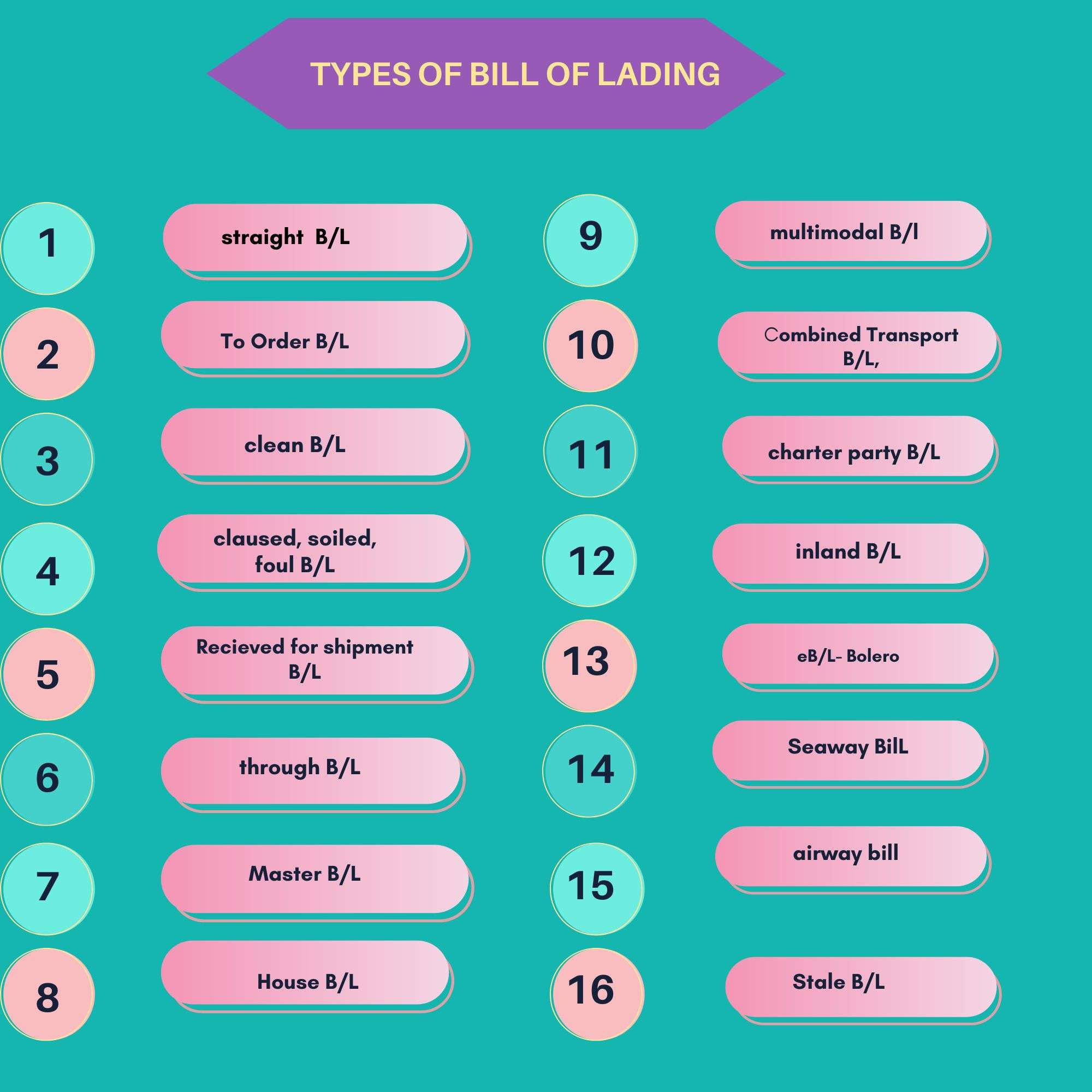
Given below are the types of bill of Lading
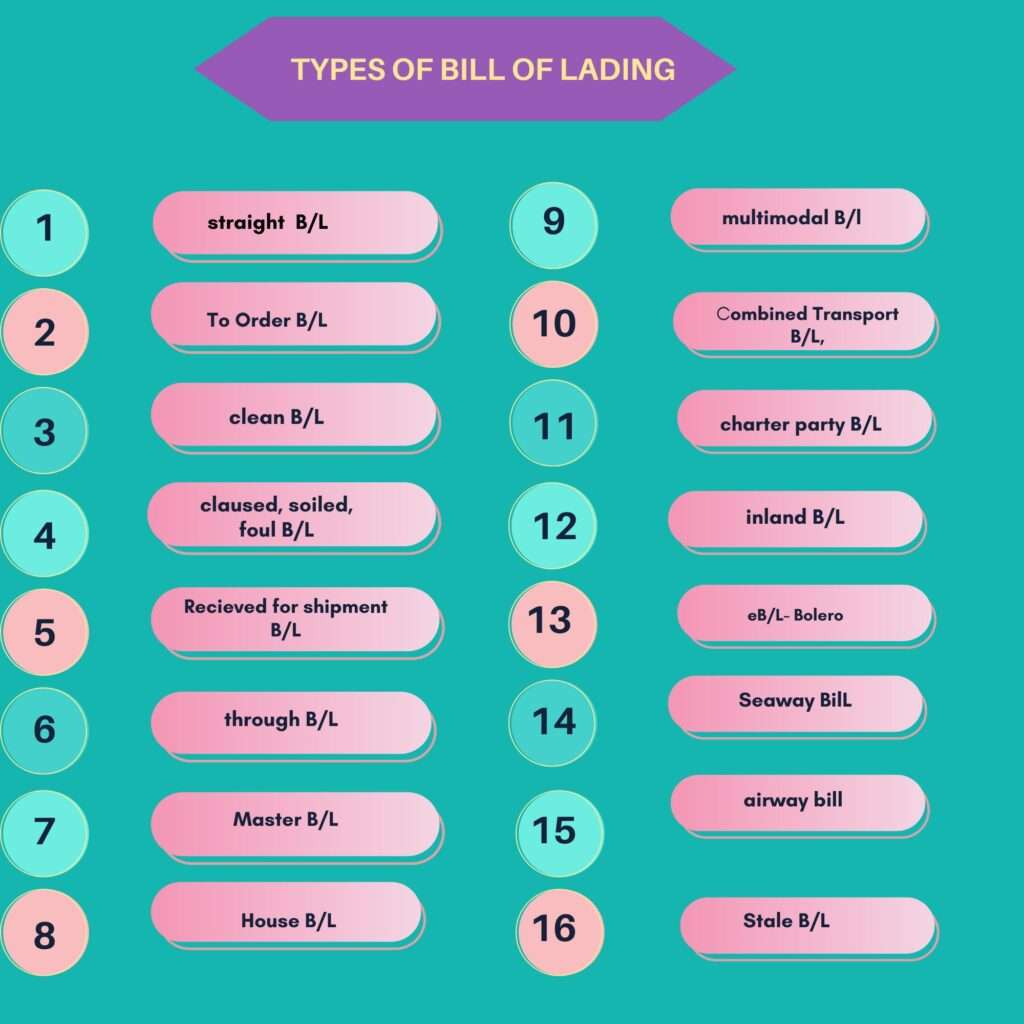
Clean Bill of Lading
A clean Bill of Lading is issued by the Shipping Company when the goods/ packages taken on Board/ stuffed in containers, is in proper order at the time of loading and does not record any defects or damages at the receipt of the goods, the bill of lading is considered clean.
In general, the payment methods, Letters of Credit and Documentary Collection transactions require a clean bill of lading. Carriers may not accept goods for transportation, if loading them would result in a soiled bill of lading, as it would require an amendment to the Letter of Credit.
Received for Shipment Bill of Lading
A received Bill of Lading is a document issued by a carrier as evidence of receipt of goods for shipment. It is given before the loading on the vessel and is not an onboard bill of lading. It is a temporary document, given before the cargo is boarded in the vessel and is not a legal document.
Through Bill of Lading
If the cargo is Pre-carried on road or rail before reaching the port of loading, a Through bill of lading is issued to the exporter. This document permits the shipping carrier to pass the cargo through several modes of transportation or several distribution centers. Depending on the destination, this bill includes an Inland Bill of Lading and an Ocean Bill of Lading.
In other words, when the shipment involves multi-model transport before reaching the place of delivery, the freight forwarder or shipping agent issues a through bill of lading
Claused Bill of Lading
A claused Bill of Lading is issued when the cargo is damaged, defective, spoiled, or if the quantity of cargo is less than mentioned.
In those cases, the shipping company will make a note about the issue or write an exception on the bill of lading of what it has been observed. The bill of lading then becomes a soiled bill of lading or a foul bill of lading or claused bill of lading
House Bill of Lading- HBL
A House Bill of Lading is a document generated by an Ocean Transport Intermediary freight forwarder or non-vessel operating company. The paper is an acknowledgment of the receipt of shipped goods issued to the shipper(exporter) when the cargo is received. This Bill of Lading is also known as the Forwarder’s Bill of Lading.
The HBL is issued when the cargo is less than container load. This is called LCL cargo.
Master Bill of Lading-MBL
A Master Bill of Lading is a document issued by shipping companies to their freight forwarders as a transfer receipt. The document specifies the terms required for transporting the freight, details of the consignor or the shipper, the consignee, and the respective person who possesses the goods.
MBL is issued by the shipping company, when there is Full Container Load (FCL) Cargo.
Charter Party Bill of Lading
A Charter Party Bill of Lading is an agreement between a charterer and a vessel owner. The vessel’s charterer issues the document to the shipper for the goods shipped on board the vessel.
Charterer is someone who wants to rent a ship, to transport cargo is called a charterer. The cargo may or may not belong to the charterer. The charterer may be transporting it on behalf of a different party.
Multimodal Transport Document/ Combined Transport Document
A multimodal Transport Document or Combined Transport Document is a type of Through Bill of Lading that involves a minimum of two different modes of transport, land or ocean. However, the modes of transportation can be anything from freight boats to air.
Stale Bill of Lading
If Bill of Lading is presented for negotiation to the nominated bank after 21 days from the date of shipment or any other date/ number of days stipulated in the documentary credit, the B/L becomes stale and is no longer a valid document. In stale B/l, the exporter will not receive payment from banks if payment method is through letter of credit.
Straight Bill of Lading
straight bill of lading is one on which the name of the consignee (the person or company who will pick up the goods at the port of destination) is specified.
A straight Bill of Lading indicates that the goods are consigned to a particular person and are not negotiable. This means that an endorse acquires no better rights than those the endorser holds. This bill is also called a non-negotiable bill of lading.
“To order” Bill of Lading
To Order Bill of Lading is one in which the name of the consignee is left blank or the term “to order” is written. This means that the bill of lading is negotiable bill of lading; in other words, it allows the sale of the cargo while it is at sea.
• This is a common occurrence in the oil business, in which it is not unusual to see a specific cargo change hands several times during a given voyage.
• In some cases, the cargo is sold to a company that wants the cargo delivered in a different port, and the shipping company is asked to arrange for that alternative.
Multimodal Bill of Lading
• The multimodal bill of lading is a document in which a carrier will arrange for the transportation and delivery of the shipment from the origin till its final destination. Because the shipment takes more than one mode of transportation, it is called “multi modal B/L” .
Multi Modal bills of lading, covers several legs of an international shipment. Multimodal bills of lading, are straight bills of lading in the majority of cases.
Combined Transport Document.
• Typically, the shipper will consign the goods to a forwarding agent at an inland collection depot.
• The Forwarding agent usually arranges the entire operation, there is likely to be more than one actual carrier and different carriers will be usually responsible for each section of the combined transport operation.
Combined transport documents can be either negotiable or non-negotiable.
• Because the combined transport documents can be issued earlier than the traditional bill of lading before the goods are shipped, a negotiable document can in theory in appropriate kinds of transaction, help to resolve the problem of the vessel arriving before the documents can catch up.
Combined Transport Document; Disadvantages
Unlikely to provide security equivalent to the shipped bill of lading.
1. Issued before the shipment and hence not a shipped bill but a received B/L
2. Different international conventions may govern each part of the operation so that carrier’s liability varies depending on where damage to the cargo occurs.
Combined Transport Document; Advantages
• The essence of the combined transport document is that one carrier usually the forwarding agent, makes himself responsible for the entire operation.
• He may subcontract each stage or more commonly each stage after the initial land leg, but he contracts with the shipper as principal.
• He is liable to shipper and if the goods are damaged on any of the three stages, he will be sued for damage caused.
• However, the forwarding agent will be able to recoup his from another carrier.
• The single contracting carrier often referred to as a Combined Transport Operator. (C.T.O)
• Combined Transport document may be issued by a N.V.O.C. (Non vessel operating carrier) such as freight forwarder.
BOLERO: Bill Of Lading Electronic Registry Organization
BOLERO IS an electronic bill of lading (eBL). It is an electronic version of the paper bill of lading with its own combination of a legal rulebook and technology which can replicate the functions of a traditional paper bill of lading.
Inland B/L
The mode of transport in an Inland Bill of Lading includes rail, road or inland waterway until the point when the exporter’s international carrier can load the items onto a ship.
In case of international consignment the exporter will need to obtain both an Inland BOL and an Ocean BOL as Inland bill only covers domestic transportation.
Air waybill (AWB)
Air waybill is issued by the air cargo carrier, after the complete consignment has been received by the carrier and the aircraft departs from the airport of departure.
Air waybill, when issued is always a non-negotiable transport document.
Buyers could collect the consignment from the carrier at the airport of destination by simply proving their identities against the company information stated on the consignee part of the air waybill
seaway bill
Also known as a Waybill, this is a type of bill of lading used for port-to-port or combined transport carriage. A waybill is identical to a bill of lading except that it is not a document of title. There are no originals issued for this type of document.
The main difference between a seaway bill and a bill of lading is that while the former is non-negotiable, the latter is negotiable.A seaway bill will show a consignor and a single consignee who can receive the goods at the port of discharge.