
A bill of lading (BL or BoL) is a legal document issued by a carrier (shipping company) to a shipper(exporter) that details the type, quantity, and destination of the goods being carried. A bill of lading also serves as a shipment receipt when the carrier delivers the goods at a predetermined destination.
A bill of lading is a document of title, a receipt for shipped goods, and a contract between a carrier and a shipper.The bill of lading is an important legal document that serves as evidence of the contract of carriage, the receipt of the goods, and the title to the goods. It also contains important information such as the description of the goods, the port of loading and discharge, the name of the carrier, and the freight charges.
Bill lading is important in ocean freight, because the exporter will have control over the goods, if importer defaults in payment and the goods will not be released to the consignee.
how the Bill of Lading is issued?
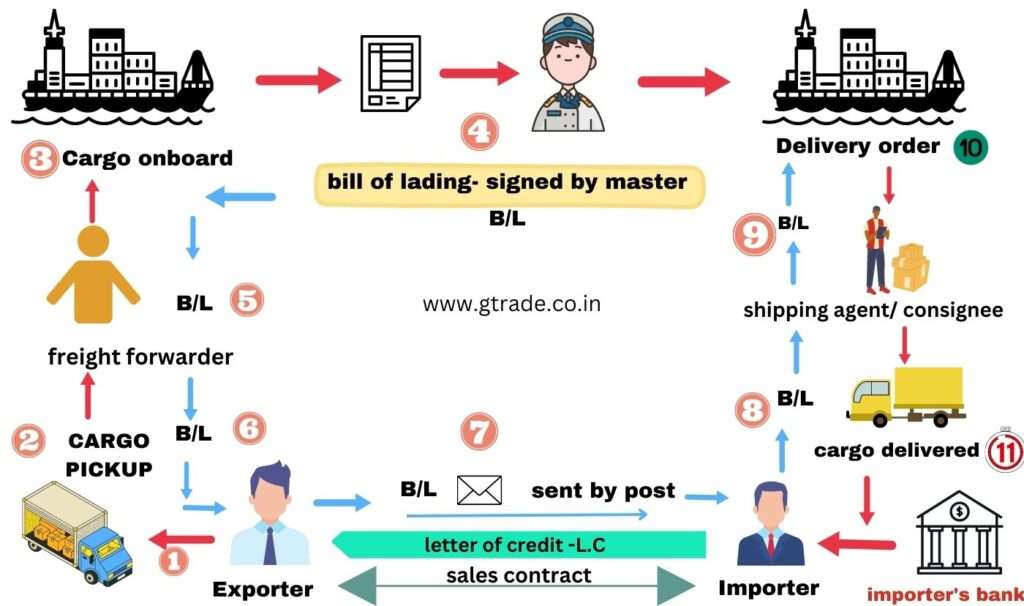
step by step process of issuing the bill of lading
- An importer and exporter enter into a sales contract, for which the importer issues a letter of credit as a guarantee for payment.
- The exporter approaches a transportation company (carrier) to ship the goods overseas.
- The freight forwarder tells the date and time of delivery of the goods to the exporter.
- On the delivery of goods on board, the person in charge of the ship hands over a receipt called as mate’s receipt to the Port Trust Authorities.
- The exporter pays the port dues to collect the mate’s receipt from the Port Trust Authorities and hands it over to the carrier’s agent.
- The carrier’s agent checks the details provided in the mate’s receipt against the goods shipped, calculates the freight accordingly, and issues the bill of lading signed by the master(captain) of the ship.
- The shipper dispatches the B/L to the bank, or to the consignee through post.
- Importers`s bank verifies the bill of lading terms to be in compliant with that of the letter of credit issued.
- The importer`s bank transfers payment to the exporter’s EEFC account and releases the B/L to the consignee.
- The consignee or the importer surrenders the bill of lading at the port of discharge to take the delivery of goods and issues a delivery order.
how many copies of B/L are issued?
It must be noted that the actual negotiable bill of lading is made in three originals, each of them is signed by the master. Out of which one is kept by the consignor(exporter) of the goods, one by the master of the ship and the last one is forwarded to the consignee(importer), who has to surrender the same, to get the delivery of the goods. On receiving the goods, the other two bills become null and void.
Key features of Bills of Lading
Bill of Lading fulfills three roles.
• 1. It is a Contract. The shipping company agrees with the shipper (the exporter), depending on the Terms of Trade (Incoterms), to transport the merchandise from one port to another for a given amount of money; it is a contract of carriage.
• 2. It is a Receipt for the Goods. When the shipping company signs the bill of lading, it is acknowledging that it has received the goods in good condition and that everything seems in proper order. The document acts as a receipt for the goods; the shipping company accepts responsibility for the goods until their port of destination.
3. It is a Certificate of Title. The document that the shipping company will need to see to authorize the release of the goods in the port of destination will also be the bill of lading. It is commonly considered that the consignee/importer, who has the original of the bill of lading is the one to which the goods belong, or that the bill of lading is a Certificate of Title.
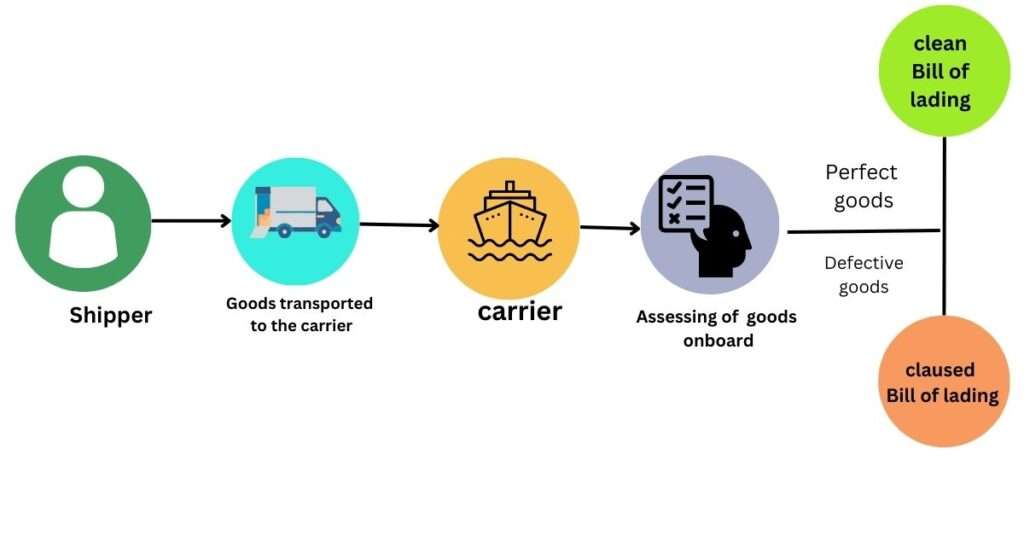
CLEAN B/L vs SOILED B/L
Clean B/L– is issued, when the shipping company finds everything in proper order at the time of loading and does not record any reservations at the receipt of the goods, the bill of lading is considered clean. In general, Letters of Credit and Documentary Collection transactions require a clean bill of lading should the bill of lading be soiled, it would require an amendment to the Letter of Credit. Carriers may not accept goods for transportation if loading them would result in a soiled bill of lading.
Soiled B/L – In some cases, if the shipping company finds something wrong with the merchandise it is picking up, (for example, the drums in which the merchandise is contained are rusty, or there are some damaged crates, or the merchandise was loaded when it was raining, or the merchandise was packaged in crates that are too weak to sustain an ocean voyage) and it does not want to assume responsibility for that condition. In those cases, the shipping company will make a note about the issue or write an exception on the bill of lading of what it has observed. The bill of lading then becomes a soiled bill of lading or a foul bill of lading.
•
- The Bill of Lading provides the seller with security against default by the buyer.
- It provides the buyer with assurance that the seller has shipped goods, before he is required to make payment.
- The delivery of the goods can be made only against the presentation of an original bill of lading,
- Transfer of the document can also transfer the right to take possession of the goods on discharge. It is for this reason is called the document of tittle.
sample copy – Bill of lading
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/bill-of-lading-01-9ea02358e8a04863b781b4fe33ff809d.jpg)

